Source: Trea
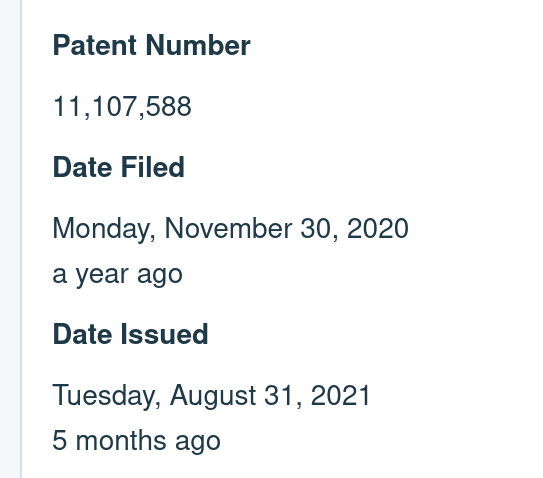
US Patent 11107588
August 31, 2021
This patent describes using vaccines as a delivery mechanism of nano-technology that measures your biometric data (heart rate, respiratory rate, temperature) and transmits it with your location to a third party
Abstract
System and methods for anonymously selecting subjects for treatment against an infectious disease caused by a pathogen. The system comprises a plurality of electronic devices comprising instructions to generate an ID and, when in proximity of another such electronic device, one or both electronic devices transmit/receive the ID to/from the other electronic device. Then, a score is generated based on a plurality of such received IDs. Additionally, based on information received from a server, relevant treatment instructions are displayed to the subjects based on the received information and the score. The server comprises instructions for sending to the plurality of electronic devices the information to be displayed with the relevant treatment instructions, additionally the server and/or the electronic devices comprise instructions to generate a prediction of likelihood of a subject transmitting the pathogen, based on the score of the subject.
Description
RELATED APPLICATIONS
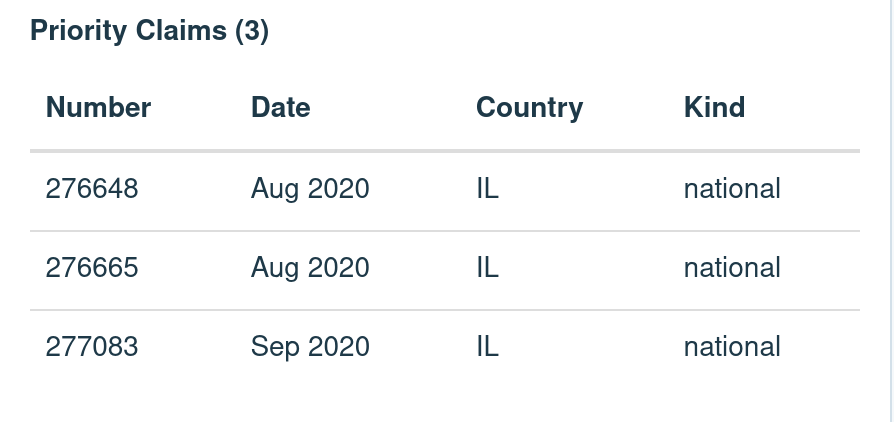
This application claims the benefit of priority of Israel Patent Application No. 277083 filed on Sep. 1, 2020, Israel Patent Application No. 276665 filed on Aug. 11, 2020, and Israel Patent Application No. 276648 filed on Aug. 11, 2020. The contents of the above applications are all incorporated by reference as if fully set forth herein in their entirety.
This application is also related to United Arab Emirates Patent Application No. P6001304/2020 filed on Sep. 17, 2020, the contents of which are incorporated herein by reference in their entirety.
FIELD AND BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention, in some embodiments thereof, relates to methods and systems of prioritizing vaccinations\treatments\testing and, more particularly, but not exclusively, to method and systems of prioritizing vaccinations\treatments\testing in a pandemic situation, whereby vaccines are at short supply and while protecting the privacy of the individuals in the population.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). It was first identified in December 2019 in Wuhan, Hubei, China, and has resulted in an ongoing pandemic. The first confirmed case has been traced back to 17 Nov. 2019 in Hubei. As of 6 August 2020, more than 18.7 million cases have been reported across 188 countries and territories, resulting in more than 706,000 deaths. More than 11.3 million people have recovered. The virus is primarily spread between people during close contact, most often via small droplets produced by coughing, sneezing, and talking. The droplets usually fall to the ground or onto surfaces rather than travelling through air over long distances. However, the transmission may also occur through smaller droplets that are able to stay suspended in the air for longer periods of time in enclosed spaces, as typical for airborne diseases. Less commonly, people may become infected by touching a contaminated surface and then touching their face. It is most contagious during the first three days after the onset of symptoms, although spread is possible before symptoms appear, after they disappear and from people who show very mild or do not show symptoms at all.
In addition, about 5% of COVID-19 patients experience complications including septic shock, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), acute cardiac or kidney injury, and disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). These complications are thought to be manifestations of the cytokine storm triggered by the host immune response of the virus. In critically ill patients, ARDS was the most common complication in 67% of the patients with a 28-day mortality of 61.5%. DIC has been widely reported in COVID-19. Pulmonary embolism (PE) in COVID-19 patients has been reported in a few studies. A recent study pointed to a higher incidence of PE with 23% in severe COVID-19 patients. The relationship between virally triggered inflammation, venous thromboembolism, and ARDS in COVID-19 is still under investigation. Given that patients with severe COVID-19 often present with shortness of breath and pulmonary infiltrates, the diagnosis of PE may be overlooked in the context of an ARDS diagnosis.
A research article by Straetemans et. al. called “Prioritization strategies for pandemic influenza vaccine in 27 countries of the European Union and the Global Health Security Action Group: a review” discussed vaccine prioritization strategies during pandemic times, but its conclusions are limited to the critical groups, for example, health care providers (e.g., doctors, nurses, laboratories, hospitals, etc.), essential service providers (e.g., police, fire fighters, public sector personnel, governmental personnel, etc.) and high risk individuals (e.g., people with high risk of complications, pregnant women, children, etc.). These obvious groups usually amount to less than 2-10% of the total population, which still leaves the government with the question of what is the best order to vaccinate the rest of the population, namely prioritizing vaccinations.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
Following is a non-exclusive list including some examples of embodiments of the invention. The invention also includes embodiments, which include fewer than all the features in an example, and embodiments using features from multiple examples, also if not expressly listed below.
read more on the trea website
Claims
- 1. A method of prophylactically vaccinating a population having a plurality of subjects with a vaccine against an epidemic infectious disease, said plurality of subjects each using a smart electronic device, the method comprising: a. a. using an ID for each said smart electronic device for determining a propensity of proximity of each said plurality of subjects; said determining a propensity of proximity comprises: i. at a proximity event, when a particular said smart electronic device of a particular said subject is in proximity of one or more other of said smart electronic devices, transmitting an ID or an indication thereof to said one or more other smart electronic devices and receiving an ID or indication thereof from said one or more other smart electronic devices, by said particular smart electronic device;said proximity event being an event where said particular said subject could, if infected, potentially infect other subjects with said infectious disease;ii. generating a score reflecting a propensity for proximity, according to a plurality of received IDs; said propensity of proximity reflecting a chance of infecting other subjects if said particular said subject becomes infected;b. generating for each said plurality of subjects a prioritization of vaccination based on said score; said prioritization being higher for subjects having a higher propensity of proximity; andc. prophylactically vaccinating particular subjects of said plurality of subjects according to said prioritization.
- 2. The method according to claim 1, wherein said using an ID comprises using an ID having fewer than 100,000 potential values.
- 3. The method according to claim 2, wherein said using an ID comprises using a unique ID and also using said ID as a portion of said unique ID.
- 4. The method according to claim 1, further comprising changing said ID periodically.
- 5. The method according to claim 1, further comprising using a second ID and transmitting said second ID or indication thereof together with said ID.
- 6. The method according to claim 5, wherein said using a second ID is carried out only at a fraction of said proximity events.
- 7. The method according to claim 6, wherein said using comprises using also second IDs previously received from others of said electronic devices.
- 8. The method according to claim 6, comprising generating an indication of closeness of a population met by said electronic device based on said received second IDs.
- 9. The method according to claim 1, wherein said score depends on an estimation of propensity of proximity of said one or more other devices.
- 10. The method according to claim 1, wherein said generating said score comprises counting the number of received IDs.
- 11. The method according to claim 10, wherein said counting comprises counting unique IDs.
- 12. The method according to claim 10, wherein said counting comprises counting IDs with a weighted parameter, said weighted parameter is generated by analyzing said transmitted second IDs.
- 13. The method according to claim 1, wherein said generating for each said plurality of subjects a prioritization of vaccination comprises transmitting said score to a server and generating said prioritization on said server.
- 14. The method according to claim 13, wherein said generating said prioritization comprises comparing scores by different ones of said electronic devices.
- 15. The method according to claim 1, wherein said generating for each said plurality of subjects a prioritization of vaccination comprises generating said prioritization on said particular electronic device.
- 16. The method according to claim 15, wherein said generating said prioritization comprises receiving from a server a list or a function indication prioritization according to score.
- 17. The method according to claim 1, comprising displaying prophylactically vaccinating instructions on said particular electronic device based on said generated prioritization.
- 18. The method of claim 1, wherein said epidemic infectious disease comprises a corona virus and wherein said prophylactically vaccinating comprises a vaccination for said epidemic infectious disease and wherein said prioritization is used to select subjects at greater risk of transmitting said epidemic infectious disease during a pandemic to be vaccinated sooner than subjects less likely to transmit said epidemic infectious disease.
- 19. The method of claim 1, wherein said ID is an anonymous ID.
- 20. The method of claim 1, wherein said (a) and (b) do not comprise providing information regarding a status related to said infectious disease in said subjects.
- 21. The method of claim 1, wherein information about said prioritization of vaccination is not transmitted outside said particular electronic device.
- 22. The method of claim 1, wherein information about said proximity event is not transmitted outside said smart electronic device or said one or more other smart electronic devices.
- 23. A system for selecting subjects for prophylactically vaccinating a population having a plurality of said subjects with a vaccine against an epidemic infectious disease, comprising: a. a plurality of smart electronic devices configured to be carried around by said subjects and configured with instructions to: i. using an ID for each said smart electronic device for determining a propensity of proximity of each said plurality of subjects; said determining a propensity of proximity comprises: at a proximity event, when in proximity of another such smart electronic device, transmitting an ID or an indication thereof to said another smart electronic device and receive an ID or indication thereof from said another smart electronic device; said proximity event being an event where a particular said subject could, if infected, potentially infect other subjects with said infectious disease;generating a score reflecting a propensity for proximity, according to a plurality of such received IDs; said propensity of proximity reflecting a chance of infecting other subjects if said particular said subject becomes infected;receiving information from a server;displaying relevant prophylactically vaccinating instructions to said subjects based on said received information;b. at least one server comprising a memory and a plurality of modules; said memory comprising instructions for: ii. sending to said plurality of smart electronic devices information usable by a circuitry in said plurality of smart electronic devices to display said relevant prophylactically vaccinating instructions.
- 24. The system according to claim 23, wherein said information comprises one or more of subject specific information.
- 25. The system according to claim 23, wherein said information comprises general information usable by a plurality of subjects and devices thereof.
- 26. The system according to claim 25, wherein said server is configured with instructions to receive scores for a plurality of said electronic devices and use said received scores to generate said general information, said electronic devices configured to use said general information to determine a relative treatment priority for their respective subjects.
- 27. The system according to claim 23, wherein said smart electronic devices comprise a proximity-detecting module using one or more of: a. physical proximity data received by means of electronic positioning data of said subject;b. a distance indicating sensor which indicates physical proximity of the location of a device in relation to the location of said another device; andc. historical location data.
- 28. The system according to claim 23, wherein said at least one server or said smart electronic devices comprise instructions to determine a prophylactically vaccination prioritization based on said propensity for proximity.
- 29. The system according to claim 27, wherein determine a treatment prioritization further comprises one or more of: a. generating a score component based on a nature of a location where said physical proximity data is related;b. generating a score component comprising health data of the subject of one or both smart electronic devices;c. generating a score component comprising a profession of the subject of one or both smart electronic devices;d. generating a score component reflecting relative health risk to said subject if said subject contracts said epidemic infectious disease; ande. generating a score component reflecting damage to society if said subject contracts said epidemic infectious disease.
- 30. The system according to claim 27, wherein when said physical proximity data is related to a location that is either indoors or in a closed space, then said score of said subject of transmitting said epidemic infectious disease increases by a factor of between about 10 times to about 100 times.
- 31. The system according to claim 23, further comprising a prophylactic vaccination server which allocates prophylactic vaccinations for a corona virus according to said prophylactically vaccinating instructions.
- 32. The system according to claim 31, wherein said server comprises a simulation module configured to perform one or both of: (a) predict the effect of vaccination on disease spread;(b) predict the effect of an ID transmission probability on distinguishing between subjects who contact mainly subjects in a same subpopulation.
- 33. The system of claim 23, wherein said smart electronic devices are configured to transmit a second ID and previously received second IDs, at a probability of less than 10% and using said received second IDs to generate said score.
- 34. The system of claim 23, wherein said transmitted ID is a non-unique ID having fewer possible values than 10% of the number of said devices.
- 35. The system of claim 23, wherein said ID is an anonymous ID.
- 36. The system of claim 23, wherein said plurality of smart electronic devices do not comprise information regarding a status related to said infectious disease in said subjects.
- 37. The system according to claim 23, wherein information about said prophylactically vaccinating instructions is not transmitted outside a particular smart electronic device.